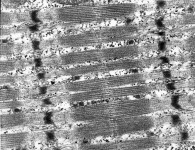
Sarcomerum (Terminologia histologica:
Sarcomerum; Myomerum)
|
Sarkomer; der im entspannten Zustand ca. 2,2 µm große Abstand
zwischen 2 Z-Linien der Skelett- oder Herzmuskulatur.
Das Sarkomer ist die funktionelle Grundeinheit der quergestreiften Muskulatur.
Bei isotonischer, d.h. mit einer Muskelverkürzung einhergehender,
Kontraktion verkürzt sich die Länge aller Sarkomere einer Muskelfaser
gleichzeitig, dabei "gleiten" die Aktin-
und Myosinfilamente ineinander. Die I-Bande
und der H-Streifen werden kürzer während
die Länge der A-Bande gleich bleibt. |
sarcomere or myomere; distance between 2 Z-lines of skeletal-
or heart muscle cells. It measures 2.2 µm
in non-contracted state and is the functional unit of striated
musculature. Under isotonic contraction, i.e. when muscle cells shorten
during contraction, the length of all their sacomeres reduces equally when
actin
and myosin filaments slide "into" each other.
Consequently, the I-band and the H-stripe
shorten while the length of the A-band does
not change. |
Schwann cellula
= Gliocytus periphericus
 Abbildungen - images
Abbildungen - images |
Schwann-Zelle; Gliazelle
des peripheren Nervensystems. Sie bildet entweder bei markhaltigen Nerven
aus vielen Wicklungen ihrer Zellmembran
um einen Nervenzellfortsatz dessen Myelinscheide (= Markscheide) oder bei
marklosen Nerven werden viele Nervenzellfortsätze
von der Zellmembran der Schwann-Zelle
umschlossen und dabei ein Stück weit in ihr Cytoplasma
invaginiert. Schwann-Zellen dienen der Ernährung und Isolation der
umschlossenen Nervenzellfortsätze, die sowohl Neuriten
als auch Dendriten sein können.
--> weitere Informationen und Abbildungen |
Schwann cell; the glial-cell
of the peripherical nervous system. In myelinated nerves
many layers of the cell membrane wind
round nerve cell processes to form the myelin sheath. In non-myelinated
nerves many nerve fibers are ensheaded by the cell
membrane of the Schwann cell. Thus they are invaginated into the cytoplasm
of this type of glial cell. Schwann cells serve for nutrition and isolation
of the related nerve cell processes that may be either neurites
or dendrites.
--> further information and images |
SER Reticulum endoplasmicum nongranulosum
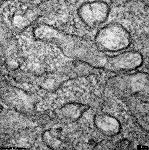
Abbildungen - images
|
glattes endoplasmatisches Retikulum; dreidimensionales
Hohlraumsystem aus Bläschen, Kanälchen und Zisternen, deren Membranen
kontinuierlich mit der äußeren Kernmembran
und selten auch mit dem Plasmalemma
zusammenhängen können, es kommt in quergestreiften
Muskelzellen als kalziumspeicherndes sarkoplasmatisches Retikulum (=
L-Tubulussystem)
vor, außerdem im Pigmentepithel der Netzthaut
und in Steroidhormon produzierenden Zellen vor.
--> weitere Informationen und Abbildungen |
agranular or smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(therefore the abbreviation SER); a complex three-dimensional network of
membranous
tubules that may be connected to the nuclear
or rarely the cell membrane. SER is
present in pigment epithelium of the retina,
steroid hormone secreting cells and in striated
muscle cells. In the latter location it serves as a storage for quick
release of calcium ions and is called sarcoplasmic reticulum or L-tubulus
system.
--> further information and images |
| Serum |
Serum; der flüssige nach erfolgter Blutgerinnung verbleibende
Teil des Blutes, der im Gegensatz zum Blutplasma
kein Fibrinogen enthält. |
blood serum; the watery portion of the blood
after coagulation, in contrast to the plasma it does not contain any fibrinogen. |
| Sinus
|
Kapillaren mit weit fenestriertem
Endothel,
z.B. als Lebersinus, oder Lymphgefäß
z.B. Marksinus oder Randsinus in Lymphknoten |
capillary, e.g. hepatic
sinus or lymphatic vessel with wide fenestrations,
e.g. medullary sinus or marginal sinus of a lymph
node |
Soma
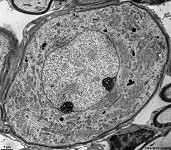
|
Perikaryon = Zellleib einer Nervenzelle
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zu Nerven,
Nervenendigungen,
Nervenfasern |
Perikaryon = cell body of a nerve
cell
--> images and information about nerves,
nerve
terminals, nerve fibres |
| Spatium |
Spaltraum, z.B. Spatium intercellulare = Zwischenzellraum |
small space, e.g., intercellular space |
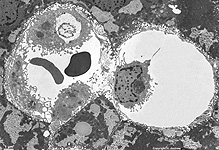
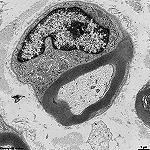
Spatium intervillosum
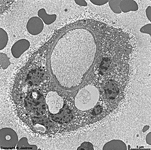
|
intervillöser Raum (wörtlich Raum zwischen den Zotten) des
Mutterkuchens (Placenta); bezeichnet den
von mütterlichem Blut durchströmten
Innenraum der Placenta in welchen die vom Embryo bzw. Fetus gebildeten
Zotten hineinreichen. Hier außen um die Plazentarzotte zu sehen.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Placenta |
intervillous space = space between the embryonal / fetal villi of the
placenta
which contains maternal blood. The image shows the intervillous space surrounding
a fetal villus.
--> images and information about the placenta |
Spatium Schmidt Lantermann
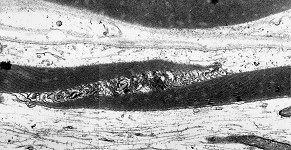
Abbildungen - images
|
Schmidt-Lantermannsche Einkerbung; in der Markscheide peripherer Nervenfasern
schräg umlaufende Auflockerungen der Markscheide. An diesen Stellen
liegen die Lamellen nicht direkt aufeinander sondern sind durch eine deutlich
erkennbare Menge Cytoplasma getrennt.
Hier finden sich Gap-junctions in den Membranabschnitten,
wodurch ein Stofftransport möglich ist. Licht- und elektronenmikroskopisch
erkennt man eine helle schräge Membranerweiterung innerhalb der Markscheide,
dei aus vielen Wicklungen der Zellmembran
einer Gliazelle gebildet wird.
--> weitere Abbildungen |
Schmidt-Lantermann-incisures; diagonal cleft in the myelin sheath of
pheripherical nerves, identified as wided
cell
membranes of Schwann cells with some
interposed cytoplasm. In these regions
gap-junctions are seen in the membranes that allow transport of smallest
particles. The gap is visible in light and electron microscopy as a light
obliquely running stripe in longitudinal sections.
--> further images |
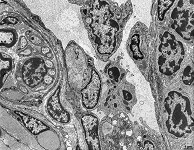
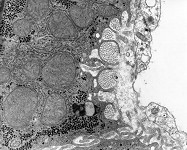
Spatium perisinusoideum Disse
Abbildungen - images
|
Dissescher Raum; enger Spaltraum zwischen den Endothelzellen
der intralobulären Kapillaren der
Leber
(Lebersinusoide) und der Zellmembran
der Leberzellen. Im Disse-Raum finden sich
neben kurzen Fortsätzen der Leberzellen auch Ito-Zellen
und retikuläre Fasern. Über
den Raum findet ein intensiver Stoffaustausch zwischen den Hepatocyten
und dem Blut statt.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Leber |
Disse's space is a narrow extracellular space located between the endothelial
cells of the liver sinusoids
and the cell membranes of hepatocytes
that border it. Ito-cells and reticular
fibres are located in this space into which the small processes of
the hepatocytes protrude. There is an
extensive exchange of substances between the hepatocytes
and the blood running through Disse's space.
--> images and information about the liver |
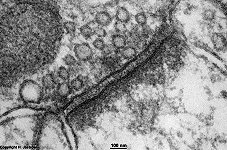
Spatium synapticum
Abbildungen - images
|
synaptischer Spaltraum, Spaltraum zwischen prä- und postsynaptischer
Membran, enthält Enzyme zum Abbau der Neurotransmitter.
--> weitere Informationen und Abbildungen |
synaptic cleft; cleft between pre- and postsynaptic membrane of a synapse.
It contains neurotransmitter degrading enzymes.
--> further information and images |
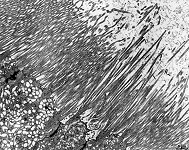
Stereocilium
Abbildungen - images
|
Stereocilie, von seiner Struktur her ein besonders langer
Mikrovillus
(4-8 µm), unbewegliche apikale Zellfortsätze, charakteristisch
für Nebenhoden und Sinneszellen
im Innenohr.
--> weitere Informationen und Abbildungen |
Stereocilium; nonmotile protoplasmic projections from the free surface
of cells resembling very long (4-8 µm) microvilli.
Stereocilia are present e.g., at the following locations: epididymal
and deferent duct, receptors cells of the inner
ear.
--> further information and images |
| Stratum |
Schicht gleichartiger Zellen in einem Gewebe |
Layer of similar cells in a tissue |
| Stratum basale endometrii |
unterste Zellschicht der Gebärmutterschleimbaut, die auf dem Myometrium
sitzt und auch nach der Abstoßung des Stratum
functionale im Zuge der Menarche (Monatsblutungen) erhalten bleibt.
Von hier auf beginnt der Wiederaufbau des Stratum functionale. |
deepest layer of the mucosa of the uterus that is located on top of
the myometrium. Only this part of the mucosa is maintained when the menstrual
bleeding swaps away the functionalis located above. The stratum basale
regenerates the Stratum functionale during the
next cycle. |
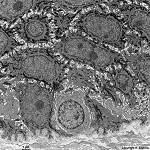
Stratum basale epithelii
Abbildungen - images
|
unterste Zelllage von Epithelgewebe
wo Mitosen vorkommen und damit der Aufbau,
bzw. die Regeneration stattfindet. |
basal layer of an epithelium. Here
mitotic
figues may be seen. From this layer the epithelium is regenerated. |
Stratum cerebrale retinae 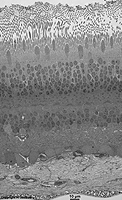 |
Der Teil der Netzhaut (Retina), der
sich entwicklungsgeschichtlich vom Zwischenhirn (Diencephalon) ableitet;
d.h. alle Schichten der Retina bis auf das Pigmentepithel und die weiter
außen liegende Choroidea.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Retina |
The part of the retina that derives
from the midbrain (diencephalon), i.e. all retinal layers apart from the
pigment epithelium and the coroidea which is located beyond it.
--> further information and images |
| Stratum compactum endometrii |
der obere, etwas dichtere Bereich des Stratum functionale
der Gebärmutterschleimhaut (Endometrium) inklusive des darauf gelegenen
Epithels. |
the upper, more dense part of the Stratum functionale
of the mucosa of the uterus (endometrium) including the epithelium located
on top. |
Stratum corneum
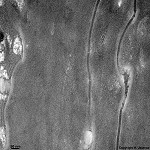
|
Hornschicht der Haut = oberste Schicht
aus abgestorbenen Epithelzellen von der
sich Schuppen abschilfern. |
corneal layer of the skin consisting
of dead epithelial cells; uppermost layer
from which the skin is flaking off. |
| Stratum fibrosum |
äußere, aus straffen parallelfaserigen Bindegewebe
bestehende relativ zellarme Schicht. Vorkommen:
1. an der Gelenkkapsel
2. im Periost
3. im Perichondrium |
outer layer consisting of tight parallel-fibred connective
tissue with few cells that is present
1. at the capsules of joints
2. in the periost
3. in the perichondrium |
| Stratum functionale endometrii |
Im Endometrium (Gebärmutterschleimhaut) derjenige (obere) Bereich,
der bei den Monatsblutungen abgestoßen und danach zur Einnistung
eines Keims wieder aufgebaut wird |
belongs to the endometrium (mucosa of the uterus) and means that portion
which is pushed off during the menstrual bleeding and regenerated thereafter
for nesting of an embryo |
Stratum ganglionare cerebelli
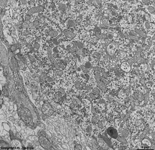
|
Ganglienzellschicht des Kleinhirns,
liegt zwischen der weiter innen gelegenen Körnerzellschicht (Stratum
granulosum) und dem weiter außen gelegenen Molekularschicht (Stratum
moleculare). In der Ganglienzellschicht finden sich die von Nervenfasern
umgebenen Kerne der Purkinje-Zellen. Die Abbildung zeigt ein Detail mit
Anschnitt einer Purkinge Zelle.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Retina |
ganglion cell layer of the cerebellum
located in between the granular cell layer (Stratum granulosum) and the
outwards oriented molecular layer (Stratum moleculare). The ganglion cell
layer contains the nuclei of the Purkinje cells which are surrounded by
nerve fibres. The image shows a detail with a sectioned Purkingje cell.
--> further images and information on the cerebellum |
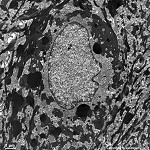
Stratum ganglionare nervi optici
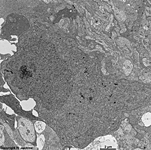
|
Ganglienzellschicht des Sehnerven;
der Bereich der Netzhaut (Retina) in dem
sich die multipolaren Ganglienzellen (3. Neuronen der Sehbahn) für
den Sehnerven befinden. Liegt unter dem Stratum
limitans internum und der Nervenfasersicht nahe dem Glaskörper.
Das Bild zeigt eine Ganglienzelle der menschlichen
Retina. |
ganglion cell layer of the optic
nerve. The multipolar ganglion cells of the optic nerve are located
in this region of the retina. These cells
are the third neurons of the visual pathway. The layer is situated close
to the corpus vitreum beyond the Stratum limitans
internum and the nerve fibre layer. The image shows a ganglion cell
of human retina. |
Stratum ganglionare retinae
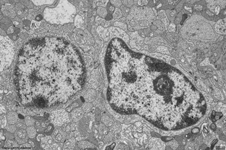
|
innere Körnerschicht der Netzhaut (Retina)
in welcher sich die
Zellkerne der Stäbchen-
und Zapfenbipolarzellen finden, die die zweiten Neurone der Sehbahn darstellen.
Diese Schicht liegt zwischen der inneren und der äußeren plexiformen
Schicht.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Retina |
inner nuclear layer of the retina.
The nuclei of the rod- and cone-bipolar cells which are the second neurons
of the visual pathway are present here. The layer is located in between
the inner and the outer plexiform layer of the retina.
--> further images and information on the retina |
Stratum germinativum

Abbildungen - images
|
Regenerations- bzw. Keimschicht der Haut,
besteht aus dem Stratum basale und dem darüber
gelegenen Stratum spinosum der Oberhaut (Epidermis).
Hier findet man besonders zwischen 0 und 4 Uhr zahlreiche Mitosen.
--> weitere Informationen und Abbildungen |
Layer of regeneration and proliferation of the skin,
consists of the
Stratum basale und the Stratum
spinosum located above which both belong to the epidermis. Mitotic
figues are seen here, most between midnight and 4 am.
--> further images and information on the skin |
| Stratum glandulo-vasculare |
Gefäß-Drüsenschicht der Haut,
bildet die Grenzschicht zwischen der Lederhaut (Corium) und der Subcutis.
Hier findet sich ein weitmaschiges Gefäßnetz aus Arteriolen
und Venolen, ferner finden sich hier im
lockeren Bindegewebe Schweißdrüsenknäule. |
vasculo-glandular layer of the skin between
the corium and subcutis containing branched plexus of blood vessels (arteriols
and venols) as well as loose connective
tissue and whirls of sweat glands. |
| Stratum granulosum
|
Epidermis: Schicht über dem Stratum
germinativum in der Keratohyalinvesikel in den eigentlichen Hautzellen
(Keratinocyten) erkennbar werden
Kleinhirn: Körnerzellschicht
breite Schicht mit Körnerzellen, Golgi-Zellen und den Glomeruli cerebellares
zwischen dem Kleinhirnmark und dem Stratum ganglionare
Ovar: Schicht hormonbildender Granulosaluteinzellen
um die weibliche Eizelle in in sekundär und Tertiärfollikeln
gut erkennbar. Lage: zwischen der Zona pellucida und der Glashaut. Die
Corona radiata ist der Teil des Stratum granulosum, der im Tertiär-
und sprungreifen Follikel die Eizelle direkt umgibt. |
Epidermis: Layer above the Stratum
germinativum in which keratohyalin vesicles become evident
Cerebellum: granular cell layer,
a broad layer containig the small granular cells, Golgi-cells and the cerebellar
glomeruli. It is located between the cerebellar medulla and the Stratum
ganglionare
Ovary: layer of hormone producing granulosalutein
cells located between the Zona pellucida of the ovum and the glass-skin
best visible in older follicles. The corona radiata which directly surrounds
the ovum is a part of this layer visible in tertiary and ripe follicles. |
| Stratum intermedium
|
auch als Stratum spinosum bezeichnet findet sich nur im unverhornten
Plattenepithel z.B. der Speiseröhre
oder Scheide als Übergangsschicht zwischen
Stratum
basale (unten) und Stratum superficiale (oben).
Morphologie der Zellen siehe Stratum spinosum. |
also termed stratum spinosum; present only in non-cornifying squamous
epithelium
e.g., in the esophagus or vagina
as intermediate zone between the stratum basale
and the stratum superficiale. Cell morphology
see stratum spinosum. |
Stratum limitans externum
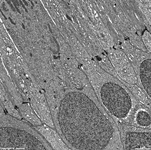
|
äußere Grenzmembran der Netzhaut (Retina).
Hier sind die Photorezeptorzellen miteinander verbunden über Zonulae
adhaerentes. Ferner gehen die Innenglieder der Photorezeptoren hier
in den übrigen Zelleib, der den Kern
enthält, über. Die quer verlaufenden sehr dunklen Bereiche in
der Abbildung gehören zum Stratum limitans externum.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Retina |
outer limiting membrane of the retina.
In this region closely above the nuclei photoreceptor cells are connected
to each other by belt desmosomes. The
inner segments of rods and cones continue here into their perikarya. The
very electron-dense areas of the image belong to the stratum limitans externum.
--> further images and information on the retina |
| Stratum limitans internum |
Direkt unterhalb des Glaskörpers beginnt die Retina
mit dieser inneren Grenzschicht, welche praktisch ihre innere Oberfläche
bildet. Durch sie hindurch lassen sich die größere Gefäße
mit dem Augenspiegel erkennen (Bild).
Darunter folgt die Nervenfaserschicht.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Retina |
This inner limiting layer of the retina is located beyond the Corpus
vitreum and forms the inner surface of the retina. Larger vessels can be
seen in opthalmoscopy because this thin layer allows the light to pass
(image). The subsequent layer
of the retinal layer is the nerve fibre layer.
--> further images and information on the retina |
Stratum lucidum
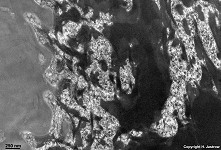
|
gut nur in der Leistenhaut erkennbar ist
diese stark lichtbrechende Schicht die Grenze zwischen Hornschicht (Stratum
corneum) und dem tiefer gelegenen Stratum
granulosum. In diesem Bereich, der nur 2 bis 3 Zellagen umfaßt,
sind die letzten Keratinocyten abgestorben; sie ist homogen eosinophil
und zeigt plattenförmig aneinander gedrängte Zellen, die keine
Kerne
mehr erkennen lassen.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Haut |
This strongly refractive layer is clearly visible only in the rippled
skin.
It is located between the Stratum corneum and the
Stratum
granulosum located beneath. In this layer, which is only two or three
cells wide, the last keratinocytes are dying. Thus this homogenous eosinophilic
layer shows compressed plate-like cells lacking nuclei.
--> further images and information on the skin |
Stratum moleculare
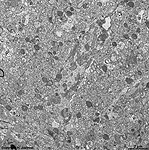
|
Im Groß- und Kleinhirn
die an der Oberfläche gelegene Schicht, welche nur noch von einer
Lage "abdichtender" Astrocyten überzogen wird. Hier finden sich neben
sehr wenig Gliazellen massenhaft intensiv miteinander verknüpfte Fasern
und nur sehr wenige Nervenzellkörper. |
molecular layer of the cerebrum and cerebellum
which is located at its surface and which is only coated by one layer of
astrocytes. It contains vast amonuts of intensively linked nerve fibres,
few glial cells and only very few nerve cell
perikarya. |
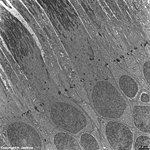
Stratum neuro-epitheliale
|
Die Gesamtheit der Photorezeptoren der Netzhaut (Retina),
also die Stäbchen und die Zapfen welche das erste Neuron der Sehbahn
bilden, liegen in dieser Schicht. Sie ist zwischen dem Pigmentepithel und
dem Stratum ganglionare gelegen und beinhaltet
von innen nach außen betrachtet folgende Schichten: äußere
plexiforme Schicht, äußere Körnerschicht, Stratum
limitans externum, Stäbchen und Zapfenschicht. Die Abbildung zeigt
nur einen Ausschnitt desmittleren bereichs des Stratum neuroepitheliale
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Retina |
This layer of the retina contains all photoreceptors, i.e. the rods
and cones which are the first neurons of the visual pathwy. It is located
between the pigment epithelium and the Stratum ganglionare.
When looking from inward to outward, the following layers are summarised
as Stratum neuro-epitheliale: outer plexiform layer, outer granular layer,
Stratum
limitans externum, Photoreceptor processes: rods and cones proper.
The image shows only a central part of the stratum neuroepitheliale.
--> further images and information on the retina |
| Stratum neuronorum piriformium |
andere Bezeichnung für das Stratum ganglionare
des Kleinhirns |
other expression for the Stratum ganglionare
of the cerebellum |
| Stratum osteogenicum |
die innere, Knochensubstanz bildende,
osteoblastenreiche
Schicht des
Periosts |
the inner layer of the periost which
contains many osteoblasts for synthesis
of bone substance |
| Stratum papillare |
Die oberste Lage der Lederhaut
(Corium). Sie ist relativ reich an ortsständigen
und freien Bindegewebszellen
(besonders Makrophagen und Mastzellen)
und enthält ein Netzwerk aus
kollagenen,
elastischen
und retikulären Fasern. Ferner findet
sich hier ein Gefäßnetz aus
dem feine Gefäße in die Papillen des Coriums emporreichen. |
The upper layer of the corium. It is rich in fibrocytes
and migrating cells of the connective
tissue such as macrophages and mast
cells. Further a network of collagenous,
elastic
and reticular fibres is present here
which embeds a vascular network giving
rise for the small vessels reaching forward into the papillae of the corium. |
Stratum pigmenti retinae
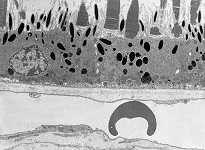
Abbildungen - images
|
Pigmentepithel der Netzhaut (Retina),
stellt die unterste Schicht derselben dar und grenzt an die Bruchsche
Membran zur Choroidea. In den hier gelegenen, schwarz erscheinenden,
Pigmentzellen
werden die hereinragenden Außenglieder von Stäbchen und Zapfen
abgebaut. Das Stratum papillare wird auch als Corpus papillare bezeichnet.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Retina |
pigmented epithelium of the retina which is the outermost layer of
the latter bordering to Bruch's
membrane of the choroidea. The outer segments of rods and cones are
invaginated into the black pigment cells
located here for their degradation. The stratum papillare is also termed
corpus papillare.
--> further images and information on the retina |
| Stratum reticulare |
auch als Corpus reticulare bezeichnet, ist der untere Abschnitt der
Lederhaut
(Corium). Hier finden sich nur relativ wenige Zellen, aber recht kräftige
gewellte, maschenartig miteinander und mit elastischen
Fasern verbundene Kollagenfaserbündel.
Das Leder hat seine derben, stabilen Eigenschaften hauptsächlich dieser
Schicht zu verdanken |
also termed corpus reticulare, is the lower part of the corium of the
skin.
Only few cells are seen here among the thick bundles of collagenous
fibres. The latter are mesh-like connected to each other with interposed
elastic
fibres. This layer is responsible for the stability of leather. |
Stratum spinosum
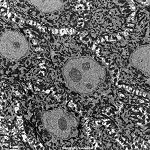
Abbildungen - images
|
Stachelzellschicht der Haut, liegt oberhalb
des Stratum basale, gehört zum Stratum
germinativum und bildet dessen oberen Anteil. Über die relativ
weiten
Interzellularräume hinweg sind
die hier vorhandenen Keratinocyten über Fleckdesmosomen
miteinander verbunden, weshalb sie den Eindruck machen als würden
sie Stachel ausbilden.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Haut |
spinous cell layer of the skin, located
above the stratum basale, belongs to the stratum
germinativum of which it is the upper part. The keratinocytes located
here are connected to each other by spot
desmosomes over the relatively wide intercellular
cleft. Thus they seem to have spines.
--> further images and information on the skin |
| Stratum spongiosum |
auf dem Stratum basale der Gebärmutterschleimhaut
(Endometrium) gelegener unterer Bereich des Stratum
functionale. Hier finden sich in der Sekretionsphase der Periode stark
erweiterte Drüsenschläuche, wodurch eine schwammartige (= spongiöse)
Struktur hervorgerufen wird |
located above the stratum basale of the endometrium
this layer forms the lower portion of the stratum functionale.
The glandular ducts located here are widened during the secretion phase
of the menstrual cycle. Thus is appears like a sponge therfore the name
sponge-like layer was given. |
| Stratum subvasculosum |
auch als Stratum submucosum bezeichnet; die oberste Schicht der Gebärmuttermuskulatur
(Myometrium), besteht aus glatten Muskelzellen
und Myofibrocyten bzw. -blasten |
also termed stratum submucosum; innermost layer of the myometrium of
the uterus, consists of smooth muscle cells,
myofibrocytes and myofibroblasts. |
Stratum superficiale
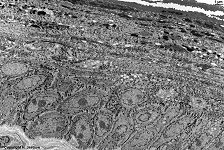
|
oberflächlichste Schicht des mehrschichtig unverhornten Plattenepithels
der Haut, die ohne feste Grenze in die daruntergelegene
Schicht, das Stratum intermedium übergeht.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Haut |
most superficial layer of the non-cornified squamous epithelium of
the skin that continious into the next layer
(stratum intermedium) without a clear border.
--> further images and information on the skin |
| Stratum supravasculosum |
äußere, dünne, überwiegend längsmuskelfaserige
Schicht der Gebärmuttermuskulatur (Myometrium) mit Verbindung zur
Längsmuskelschicht des Eileiters
und der Scheide (Vagina). |
thin, mainly longitudinally oriented smooth
muscle fibres are present in this outer layer of the myometrium of
the uterus. The muscle fibre bundles continue into the layers of longitudinal
smooth musculature of the fallopian tube
or vagina. |
| Stratum synoviale |
innerste Schicht der Gelenkkapseln, hier wird von Becherzellen
die Gelenkflüssigkeit (Synovia) gebildet. |
innermost layer of the capsule of joints with goblet
cells that secrete the fluid of joints, the synovia. |
| Stratum vasculosum |
Gefäßschicht; Bezeichnung für die gefäßreiche,
mittlere Schicht der glatten Muskulatur
der Gebärmutter (Myometrium). Hier finden sich neben meist ringförmig
verlaufenden Bündeln glatter Muskulatur muskuläre Arteriolen
und ein Venolengeflecht |
vascular layer; term for the mid layer of the myometrium which is rich
in vessels. Apart from usually cirular bundles of smooth muscle cells there
are mucsular arteriols and a plexus
of venols. |
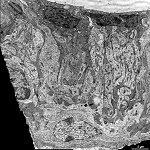
Stria vascularis
Abbildungen - images
|
gefäßführende Schicht des Corti-Organs im Innenohr,
die für die Produktion der Endolymphe verantwortlich ist. Hier finden
sich chromophile (dunkle), chromophobe (helle) und Basalzellen. Die Stria
vascularis ist das einzige Epithel,
das Kapillaren enthält. |
vascular layer of the organ of Corti in the inner
ear responsible for production of endolymph. The cells encountered
here are chromophil (dark), chromophob (light) or basal cells. The stria
vascularis is the only epithelium
that contains capillaries.. |
| Stroma |
bindegewebiges Stützgewebe eines Organs oder Tumors, welches die
funktionstragenden Zellen (das Parenchym) umgibt. Das Stroma besteht aus
Bindegewebszellen
und -fasern. |
connective tissue of an organ or tumor surrounding the function-bearing
cells (the parenchyme). The stroma consists of connective
tissue cells and fibres. |
Substantia fundamentalis

|
Grundsubstanz; der ungeformte, aus Glykosaminoglykanen (v.a. Hyaluronsäure)
bestehende Teil der Interzellularsubstanz. Ihre Entmischung ist Initialvorgang
der Bindegewebsalterung (Asbestfasern). Die Abbildung zeigt die Grundsubstanz
um eingebettete kollagene und elastische
Fasern.
--> Abbildungen und weitere Informationen |
ground substance, the amorphous part of the intercellular substance,
it contains glycosaminoglycans. In the ageing process it decombines. The
image shows collagen and elastic
fibres embedded in ground substance.
--> further images and information |
| Substantia intercellularis |
Interzellularsubstanz; von Körperzellen gebildete und in den Interzellularraum
ausgeschiedene, dem Gewebeaufbau dienende Stoffe, die sich zum Teil zu
kollagenen,
elastischen
und retikulären Fasern zusammenfügen
teils strukturlos bleiben und das Binde- bzw. Einschlußmittel für
die Fasern bilden. |
intercellular substance; composed in cells and secreted to the intercellular
cleft; it helps the tissue to arrange, it contains reticular,
collagen,
elastic
fibres and amorphous parts. |
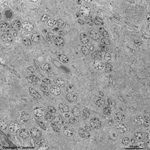
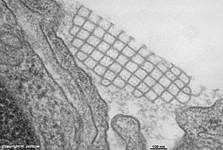
Surfactant
|
Der Surfactant stellt einen Proteinphospholipidfilm, der hauptsächlich
aus Lecithin besteht, dar. Dieser Flüssigkeitsfilm überdeckt
die gesamte Oberfläche der Lungenbläschen
(Alveolen) und dient der Herabsetzung der Oberflächenspannung der
Lungenalveolen, was für den Gasaustauch sehr wichtig ist; gebildet
wird er von Clara-Zellen und von Pneumozyten
vom Typ II. Die in ihm enthaltenen Phospholipide können sich, besonders
in Nischen, miteinander vernetzen. Diese Vernetzungen werden als tubuläres
Myelin (Abbildung) bezeichnet und sind nicht mehr oberflächenaktiv.
Sie werden von Alveolarmakrophagen
phagocytiert und abgebaut. Auch Pneumozyten vom Typ I können mittels
Pinocytose
Surfactant abbauen. Die Halbwertszeit von Ausscheidung bis Abbau beträgt
14 bis 24 Stunden.
--> Informationen und Abbildungen zur Lunge |
The surfactant is a mixture of proteins and phospholipids consisting
mainly of lecithin. It covers the entire surface of the alveols of the
lung
and reduces the tension of the surface, which is very important for the
exchange of respiratory gases. It is synthetised in Clara-cells and alveolar
epithelial cells of the type 2. Its phospholipids may aggregate in small
recesses as tubular myelin (image), which is no longer surface-tension
active. Aggegates of tubular melin are removed by
phagocytosis
by alveolar macrophages which incorporate and degrade the material. Surfactant
is also resorbed by alveolar epithelial cells of the type 1 by means of
pinocytosis.
Half-life of the surfactant, i.e. the time from secretion to resorption
is 14 to 24 hours.
--> further images and information on the lung |
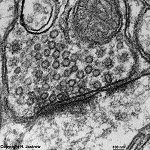
Synapsis
Abbildungen - images
|
Synapse; Umschaltstelle für die diskontinuierliche Erregungsübertragung
von einem Neuron auf ein anderes oder auf
das Erfolgsorgan, die Erregungsübertragung kann chemisch und elektrisch
an gap-junctions erfolgen.
--> weitere Informationen und Abbildungen |
Synapse, the space between the junction of two neurons
in a neural pathway or a neuron and an organ,
the electrical impulse running down an axon either causes a chemical neurotransmitter
release or an electrical impulse via ion diffusion at gap-junctions.
--> further images and information |
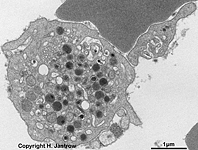
Systemum canaliculare apertum
|
Offenes canaliculäres System; ist aus Invaginationen der Blutplättchenmembran
hervorgegangen und bleibt mit der Umgebung in offener Verbindung, es enthält
leicht elektronendichtes Material.
--> weitere Informationen und Abbildungen
von Thrombocyten |
System of smooth interconnensted tubules; it develops from invaginations
of the outer "cell" membrane, it keeps
in touch with the outer space and contains slightly electron-dense material.
--> further images and information on
thrombocytes |
-->