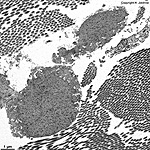
Fibra elastica
|
Elastische Faser; sie sind verzweigt und bilden Netzwerke in der extrazellulären
Substanz des Bindegewebes, sie bestehen aus
12 nm dicken Mikrofibrillen und einem "Kern" aus Elastin. Das Elastin ist
von amorphem Material umgeben, das viel Glycin, Prolin und etwas Hydroxyprolin
enthält.
--> Abbildungen und weitere Informationen |
Elastic fibre; these fibres of the extracellular substance in connective
tissue are built around a microfibrillar scaffold (12 nm in diameter)
the centre consists of elastin. The elastin is surrounded by amorphous
material containing glycine, proline and some hydroxyproline.
--> further images and information |
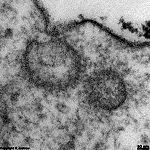
Endocytosis
|
Endozytose; Stoffaufnahme in die Zelle durch örtliche Einstülpung
der Zellmembran um das Substrat. Das
so entstehende Bläschen wird in das Zellinnere aufgenommen.
--> weitere Abbildungen und Informationen |
Endocytosis; a method of ingestion of a substance into a cell. The
membrane
invaginates to form vesicle that transports the material into the cell.
--> further images and information |
| Endomysium |
lockeres, Kollagenfibrillen Typ 3
reiches Bindegewebe innerhalb eines Primärbündels
der Skelettmuskulatur, d.h. direkt im Anschluß
an die Basallamina um die einzelnen
Muskelzellen
herum gelegen ist; enthält neben geschlängelten
Blutkapillaren
auch die zu den motorischen Endplatten
laufenden Nervenfaserendigungen. |
loose connective tissue with mainly collagen
fibrils of type 3 in a primary bundle of skeletal
muscule tissue, located directly beneath the basal
lamina of the muscle cells, contains
curved capillaries and nerve
fibre terminals running to nearby motor
end plates. |
| Endoneurium |
Endoneurium; das Bindegewebe zwischen peripheren
Nervenfasern;
enthält zahlreiche Blutkapillaren |
Endoneurium; a delicate connective tisue
sheath that surrounds nerve fibers within
a fascicle; contains many capillaries. |
| Endosteum |
Endost; die dem Periost vergleichbare, aber dünnere und lückenhafte
Bindegewebshaut,
die die Markhöhle eines
Knochens auskleidet. |
Endosteum; the small connective tissue
membrane lining the medullary cavity of a bone. |
| Endotendineum |
Endotendineum; das gefäß- und nervenführende Bindegewebe
zwischen Vagina fibrosa und Vagina synovialis der Sehnenscheide. |
Endotendineum; the connective tissue in between the fibrous and synovial
sheath of a tendon. |
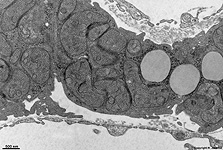
Endotheliocytus
fenestratus
|
fenestrierte Endothelzelle einer Blutkapillare.
Die fenestrierten Endothelzellen liefern mit ihrem auf beiden Seiten von
Zellmembran
begrenztem Cytoplasma keine kontinuierliche
Abgrenzung für die von ihnen ausgekleidete Kapillare. An den so entstehenden
feinen Löchern oder Poren können sehr leicht Stoffe aus dem Lumen
an die Basallamina unterhalb des Endothels
herantreten. Zum Teil werden die Poren jedoch von einer sehr zarten Membran
überzogen, die diesen direkten Kontakt verhindert.
--> Endothelzellen |
Fenestrated endothelial cell of a
blood capillary. Such endothelial cells
provide no continous bordering of a capillary lumen with their cytoplasmic
processes surrounded by their cell membranes.
The resulting pores allow substances from the capillary lumen to contact
the underlaying basal membrane more easily. On some locations the pores
are covered by thin membranes inhibiting direct contact to the basal
lamina.
--> endothelial cells |
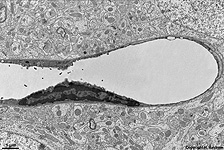
Endotheliocytus
nonfenestratus
|
nicht fenestrierte Endothelzelle,
die die Wand eines Blutgefäßes
kontinuierlich gegen die unterhalb der Endothelzelle gelegene Basallamina
abgrenzt. Wichtig ist dies z.B. bei der Blut-Hirn
Schranke.
--> Endothelzellen |
Non-fenestrated endothelial
cell that has no pores and forms a continous border to the lumen of
a blood vessel, i.e. the underlaying basal
lamina cannot be reached quite easily. This is important e.g. for the
blood-brain
barrier. |
| Epimysium |
aus Bindegewebe mit Kollagenfasern
gebildete Hülle, die einen gesamten Skelettmuskel
umfaßt und nach Innen in das Perimysium
externum übergeht, verbindet dieses nach Außen mit der Faszie
des Muskels. Im Epimysium liegen Arteriolen,
Venolen
und Nervenfasern. |
sheath consiting of connective tissue that
covers a whole skeletal muscle and continues
into the external perimysium on one hand and on the other hand into the
fascia of the skeletal muscle. It contains arterioles,
venoles
and nerve fibres. |
| Epineurium |
Epineurium; Bindegewebe, welches
einen gesamten größeren Nerven
umgibt. Außen ist es straffes Kollagenfaser-reiches
Bindegewebe nach Innen geht es in lockeres Bindegewebe über, zeigt
univakuoläre
Fettzellen und setzt sich in das Perineurium
fort. Im Epineurium finden sich deutlich weniger Arteriolen
und Venolen als z.B. im Epimysium. |
Epineurium; connective tissue sheath of
a whole nerve. Whereas the outer portion
consists of tight collagen-fibre-rich connective tissue, the inner portion
is a loose connective tissue with unilocular
fat cells that continues into the Perineurium.
The epineurium shows considerably less arterioles
and venoles than e.g., the epimysium. |
| Epitheliocytus |
Epithelzelle, Zelle eines Epithels. |
Epithelial cell, cell of an epithelium. |
| Epitheliocytus
cuboideus |
kubische, isoprismatische oder würfelförmige Epithelzelle. |
cuboid or isoprismatic epithelial
cell. |
Epitheliocytus
caliciformis
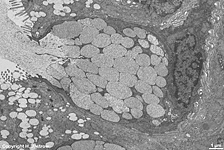
|
Becherzelle, schleimproduzierende Drüsenzelle, die
zwischen Säulenepithelzellen des Respirationstrakts
(z.B. Nase, Trachea,
Bronchien)
und im Darm (Dünndarm bis Dickdarm)
vorkommt. Die Muzinproteine werden im RER synthetisiert,
von dort in den
Golgi-Apparat transportiert.
Hier werden sie mit Zukerketten gekoppelt (O-Glykosylierung) und kontinuierlich
langsam eher peripher oder nach Stimulation sehr schnell von zentral her
abgegeben, wie in der Abbildung zu erkennen ist. Becherzellen sind ekkrine,
muköse, unizelluläre Drüsen. |
goblet cell, mucous secreting gland cell located in between
columnar epithelial cells of respiratory
tract (e.g., nose, trachea,
bronchies)
or in gut (duodenum to colon).
The mucin proteins are produced in the RER
and transported to the Golgi-apparatus.
Here they are linked to sugar chains by O-glycosylation and slowly secreted
in more peripherical parts of the cell or quickly released after stimuli
from the central area as shown in the image. Goblet cells are eccrine,
mucous unicellular glands. |
| Erythrocytus reticularis |
Reticulozyt, die letzte noch kernhaltige
Zelle aus welcher sich in der Erythropoese die roten
Blutkörperchen bilden. Retikulocyten erscheinen normalerweise
nicht im Blut des Menschen sondern sind im
blutbildenden roten Knochenmark zu finden. |
Reticulocyte, the last precursor cell in erythropoesis that has a cell
nucleus.
After degradation and extrusion of this nucleus it becomes a mature erythrocyte.
Reticulocytes are not seen in normal human blood but exist in the red bone
marrow which is responsible for haematopoesis. |
Erythrocytus
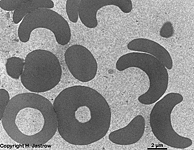
|
Erythrozyt; = "rotes Blutkörperchen"; eine bikonkave kernlose
und zellorganellenfreie Scheibe; Durchmesser
7,5 µm; kernlos; enthält Hämoglobin, welches Sauerstoff
(O2) bzw. Kohlendioxid (CO2) durch den Körper
transportiert.
--> weitere Informationen und Abbildungen |
Erythrocyte; the mature red blood cell, or corpuscle containing neither
a nucleus nor any cell
organelles; biconcave disk 7,5 µm in diameter; contains hemoglobin,
transporting oxygen (O2) or carbondioxide (CO2) through
the body.
--> further images and information |
Euchromatinum
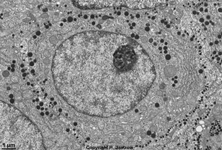
|
Euchromatin; der aktive Teil des Chromatins; im Interphasekern infolge
der Entspiralisierung der DNA nur schwach anfärbbar. Hier findet die
Transkription statt; d.h. die Erbinformation wird auf eine Boten-Ribonucleinsäure
kopiert.
--> Abbildungen und weitere Informationen |
Euchromatin; unfolded or uncondensed portions of chromatin during interphase.
Here the transcription of DNA information to messenger ribonucleicacid
takes place.
--> further images and information |
Exocytosis

|
Exozytose; das Ausschleusen von in Vesikeln
befindlichen Stoffen aus der Zelle; durch Verschmelzung der Vesikelmembran
mit der Zellmembran wird der Vesikelinhalt
in den Extrazellularraum abgegeben.
--> Sekretvesikel |
Exocytosis; the discharge of cellular secretory
vesicles into the extracellular space. The vesicle membrane fuses with
the cell membrane thus releasing vesicle
content.
--> secretory vesicles |
--> 









