Overview rough endoplasmic reticulum
(RER):
Pages with explanations are linked to the
text below the images when available
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
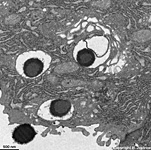
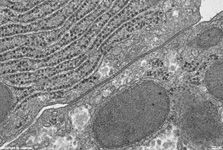
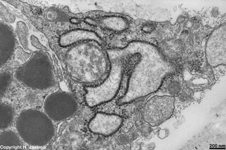
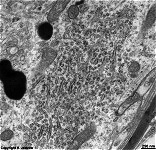
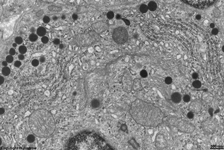
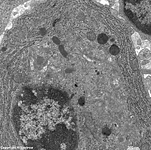
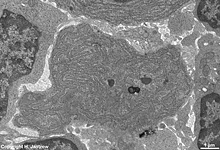
human plasma cell RER, pharyngeal
tonsil (Tonsilla pharyngea) |
detail:
cytoplasm |
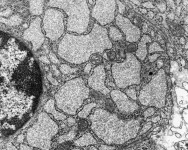
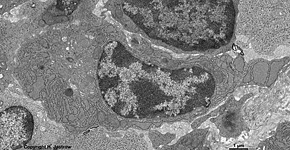
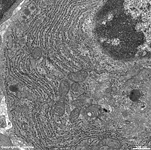
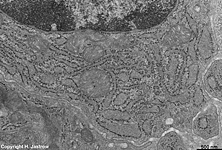
human plasma cell RER 2
Tonsilla pharyngea |
detail 1:
cytoplasm |
detail 2:
RER |
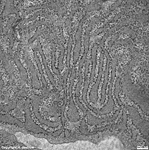
detail 3:
RER |
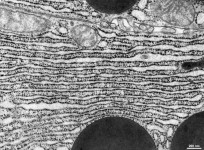
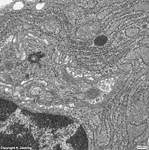
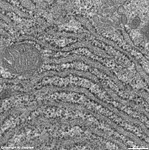
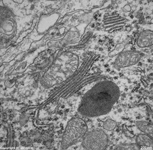
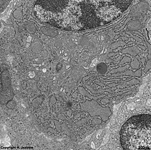
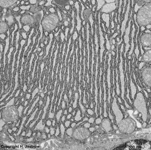
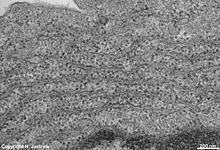
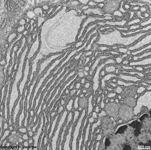
parallel RER,
parotid gland (rat) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
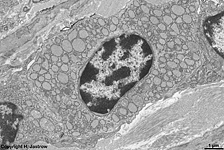
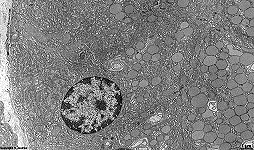
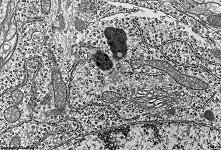
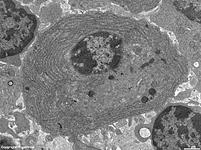
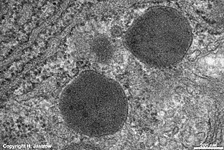
human plasma cell
with RER |
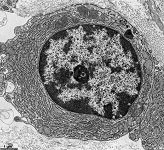
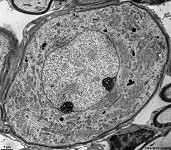
plasma cell: RER
(human) |
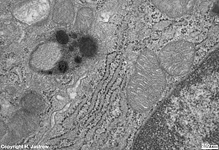
RER + lipofuszin-
vesicle, human plasma cell |
RER of a human
plasma celll |
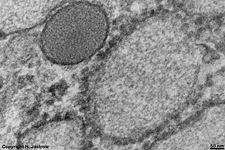
RER + primary lysosomes
of a human plasma cell |
partly dilated RER,
parotid gland (rat) |
The rough- or granular endoplasmic reticulum
(Terminologia histologica: Reticulum endoplasmicum granulosum) is a complex
tree-dimensional
network of lamellas (Terminologia histologica:
Lamellae), attached
saccules (Terminologia histologica: Sacculi),
membranous
tubules and flat
cisterns (Terminologia
histologica: Cisternae).
Ribosomes
are bound to its outer surfaces in more or less regular pattern. The lumen
(Terminologia histologica: Lumen) is bordered by membranes (Terminologia
histologica: Membranae) and is extremely rich in proteins (concentration:
200 g per litre). All RER membranes have an outer surface (cytosolic surface;
Terminologia histologica: Facies externa) directed towards the cytoplasm
and an inner surface (luminal surface; Terminologia histologica: Facies
interna) bordering the lumen. The paired membranes of the RER have
a distance of 20-60 nm. Local dilatation of the RER is seen
when high protein synthesis and storage is necessary. The RER membranes
may be outfoldings of the outer nuclear membrane,
resulting in a continuity of perinuclear space (space between
outer
and inner nuclear membrane)
and RER lumen.
RER collects, modifies, stores and transports proteins that
are synthesised by the ribosomes anchored
to the outer membrane of the RER. Many of these proteins are not for the
cell itself but for secretion. In cells of
glands,
but also in most polar cells the RER is located more basally, followed
by a Golgi-zone while above the latter the
secretion vesicles accumulate in the apical
cytoplasm.
RER forms small vesicles that are transported either to the
Golgi-apparatus
or to the cell membrane. The proteinaceous
content of these vesicles is released after membrane fusion.
The greater the protein synthesis of a cell, the higher its content
in RER. High amounts are usually seen in plasma
cells, exocrine pancreas cells, neurons,
osteo-,
chondro-
and fibroblasts.
A continuity of rough into smooth ER is possible
and may be seen e.g., in cells of the liver.
In neurons, RER occurs in parallel membrane
plates and is associated with free ribosomes
as Nissl-body (chromatophilic substance or Tigroid-substance;
Terminologia histologica: Substantia chromatophilica).
In light microscopic stains RER is basophilic since its ribosomes
bind messenger ribonucleic acids; RNAs. The latter carry the genetic information
for the amino acid sequences of proteins synthetised in the RER in the
process of translation.
Further detailed information is available in the professional
version of this atlas.
--> smooth ER, ribosomes,
cytoplasm,
Golgi-apparatus,
nuclear
membrane, secretory vesicles, plasma
cells
--> Electron microscopic atlas Overview
--> Homepage of the workshop
Three pictures were kindly provided by Prof. H. Wartenberg;
further images, page & copyright H. Jastrow.