| differential diagnosis |
striated |
smooth |
| characteristics: |
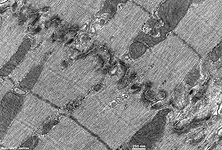
skeletal
muscle
|
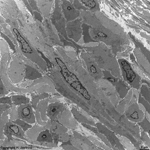
heart
muscle
|
smooth
muscle
|
| sample image
(for more images
click the name
above the image,
please) |
|
|
|
| nuclei |
very many, close to cell membrane |
1-2, rarely more located centrally |
only 1 in the centre of the cell |
| nuclear diameter and form |
8-10 µm, lens-like |
~ 12 µm, ovoid |
10-25 µm, rod-like, corkscrew-like when contracted |
| order of filaments |
exactly parallel (striation) |
exactly parallel (striation) |
net-like (no striation) |
| Cohnheim fields |
yes |
yes |
no |
| cell form and length |
cylindric, up to 15 cm |
Y-like branched, 50-120 µm |
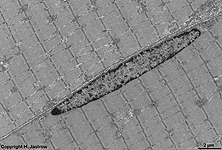
spindle-like, 50-200 µm, in uterus
maximal 700 µm |
| tubular system |
Triads: L-T-L tubules |
Dyads: L-T or T-L tubules, rarely triads |
none |
sarkoplasmatic reticulum
= L-tubules |
very many |
many |
not present but caveolae |
| mitochondria |
small, electron-dense, many |
very large, electron-dense, very many |
small, less electron-dense, rare, only close to nuclei |
| power |
very strong |
moderate |
small, shorten about 20 % of total length |
| duration |
only some minutes of full power |
never ending change of contraction & release |
contraction for hours possible |
| innervation |
controlled by mind |
autonomous |
autonomous, low frequency of own activity |
| stimulation |
controlled by motor neurons |
influenced by autonomic nerves
(& hormones) |
influenced by autonomic nerves
& hormones |
| motor end plates |
present |
none, stimuli conducted by gap-junctions |
none, stimuli conducted by gap-junctions |
| regeneration |
possible thanks to satellite
cells |
none in practice (no satellite
cells) |
easy by mitosis |
| specialities: |
Type 1 fibres = red fibres
higher endurance, much myoglobin, thinner
Type 2 fibres = white fibres
faster, less myoglobin, thicker |
striated discs |
caveolae, dense
plaques, dense bodies,
synthesis of prostacycline and elastic fibres |






