Oocytus
Abbildungen - images
|
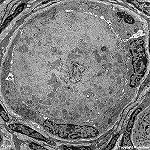
Eizelle weibliche Keimzelle; entwickelt sich aus diploiden Urkeimzellen
(Oogonien) im Ovar durch Oogenese und Follikelreifung zur befruchtungsfähigen
Gamete mit einfachem (haploiden) Chromosomensatz
(23 Chromosomen). Die nach der Ovulation vom Eileiter
aufgenommene Eizelle ist von einer Membran (Zona pellucida) und einer Schicht
aus Granulosaluteinzellen, der Corona radiata umgeben. Die Eizelle ist
die größte menschliche Zelle überhaupt und hat einen Durchmesser
von 130 - 150 µm. Im Durchschnitt reifen im Leben einer Frau nur
etwa 500 Eizellen vollständig heran, denn ein Großteil geht
während der Entwicklung zum sprungreifen Follikel zugrunde.
--> weitere Abbildungen |
Ovum; the female reproductive cell. It develops from an oogonium that
undergoes a process of maturation, during which primary and secondary oocytes
are produced, finally giving rise to the mature ovum. During this process,
the number of chromosomes is reduced
from 46 to 23. When a follicle disrupts the ovum is released with the granulosalutein
cells (Corona radiata) and the membrane (Zona pellucida) surrounding it.
It is transported through the fallopian tube
to the uterus. The ovum is the largest human cell with a diameter of 130
- 150 µm. On an average, only 500 ovi can be fertilized since the
majority gets atrophic before reaching the final stage.
--> further images |
Osteoblastocytus
Abbildungen - images
|
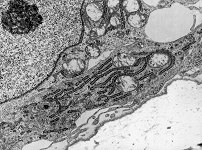
Osteoblast; knochenbildende Zelle, geht aus Mesenchymzellen hervor.
Sie bilden die unverkalkte Interzellularsubstanz des Knochens,
in die sie sich allmählich selbst einmaueren. Sobald sich die Zellen
eingemauert haben, werden sie weniger stoffwechselaktiv und dann als Osteocyten
bezeichnet. Osteoblasten werden durch das in den C-Zellen der Schilddrüse
gebildete Hormon Calzitonin und Vitamin D3 stimuliert, was zu vermehrtem
Kalziumeinbau in den Knochen und damit zur Senkung des Blutkalziumspiegels
führt. Das in der Nebenschilddrüse synthetisierte Parathormon
hemmt sie.
--> weitere Abbildungen |
Osteoblast; a cell of mesodermal origin responsible for bone
formation. Osteoblasts secret the intercellular substane of bone into which
they immure themselves. With increase of bone substance and calcification
the cells reduce their activity and become osteocytes. Osteoblasts are
stimulated by the hormone calcitonin (deriving fron the C-cells of the
thyroid
gland) and vitamin D3 resulting in an increased calcification of the
bone matrix and a decrease of the blood calcium level. The parathormone
of the parathyroid glands inhibits activity of osteoblasts.
--> further images |
| Osteoclastocytus |
Osteoklast; riesige (ca. 100 µm im Durchmesser große) vielkernige
Zelle, die aus vielen miteinander verschmelzenden Monocyten
hervorgeht, die aus Kapillaren stammen.
Sie liegen in den von ihnen gebildeten "Fraßlöchern", den Howshipschen-Lakunen.
Ihre Aufgabe besteht darin dem Knochen
beim Wachsen in die richtige Form zu fressen, sei es beim Neuwachstum oder
bei der Reperatur eines Bruches. Die Zellen werden durch Parathormon stimuliert
und durch Vitamin D3 und das Hormon Calzitonin gehemmt. Da sie für
den Abbau des als Kalziumspeicher dienenden Knochens verantwortlich sind,
spielen sie eine wichtige Rolle in der Erhöhung des Blutkalziumspiegels. |
Osteoclast; a giant (about 100 µm in diameter) multinuclear
cell originating from fusion of several monocytes
that evade nearby capillaries. Osteoclasts
are found in pits (Howship`s lacunae) on the surface of the bone.
It resorbs excess bone tissue in the process of remodeling of growing bones,
or damaged bone during repair of fractures. Osteoclasts are stimulated
by parathormone and inhibited by calcitonin and vitamin D3. Their activity
increases the blood calcium level since they serve in destruction of bone
the most important calcium storage of the body. |
Osteocytus
Abbildungen - images
|
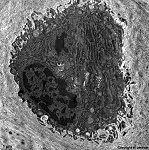
Osteozyt; aus den Osteoblasten hervorgegangene nur noch wenig stoffwechselaktive
Knochenzellen, die in kleinen Lakunen liegen. Sie strecken ihre Protoplasmafortsätze
weit in den Knochen hinein und stehen über diese sehr dünnen
unbeweglichen Fortsätze miteinander in Verbindung. Die die Knochensubstanz
durchziehenden Pseudopodien ernähren die Zellen. Letztere ordnen sich
in typisch rundlicher Weise um die Kapillaren
des Knochens (Haverssche Kanäle) an und bilden dessen funktionelle
Grundeinheit, das Osteon.
--> weitere Abbildungen |
Osteocyte; a mesodermal bone-forming cell that has become entrapped
within the bone matrix. It lies within a lacuna. Immobile cell processes
extend outward through canaliculi for communication to other osteocytes
and reach the capillary of bone tissue
located in the canal of Havers. Thus bone is a living tissue. The circular
apposition of bone lamellae around a canal of Havers is the functional
unit of the bone called osteon.
--> further images |
--> 





