 |
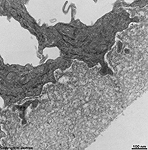
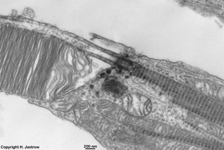
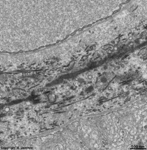
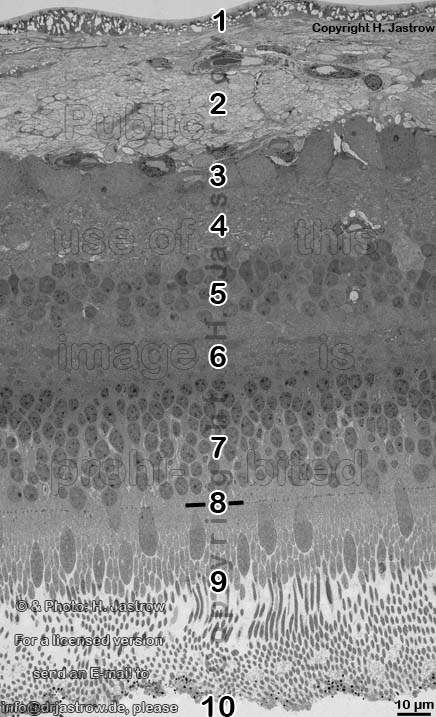
1. inner limiting membrane
= Stratum limitans internum (--> images)
borders the vitread body (Corpus vitreum) with a basal
lamina which has considerable regional differences in thickness,
radial
fibres spread above the basal lamina which are the endings ofMüller
Glial cells. They are connected to each other via small
tight
junctions just above the basal lamina.
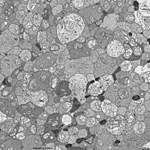
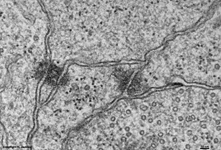
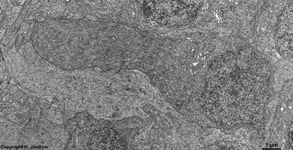
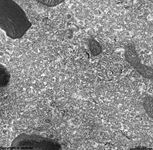
2. nerve fibre layer
= Stratum neurofibrarum (--> images)
virtually all non-myelinated axons
which form the optic nerve at the papilla, further some blood
vessels are present here
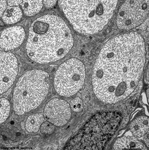
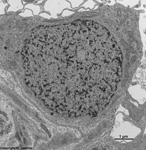
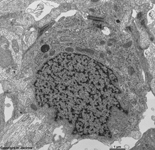
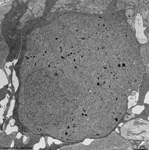
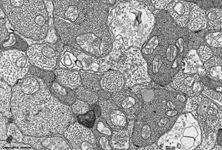
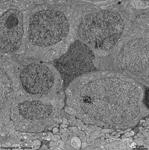
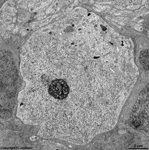
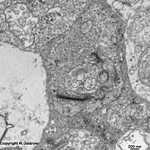
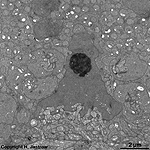
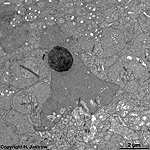
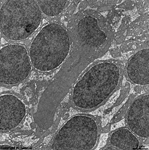
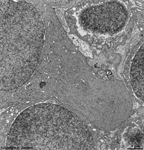
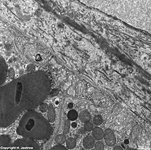
3. ganglion cell layer
=
Stratum
ganglionicum (--> images) with multipolar
ganglion
cells, which are the third neurons of the visual pathway
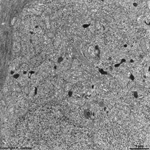
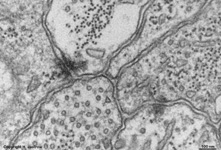
4. inner plexiform layer
= Stratum plexiforme internum (--> images)
contains the synapses between the second (bipolar cells) and the
third neurons (ganglion cells) of the visual pathway. Most of these synapses
are ribbon synapses with synaptic bodies,
further many conventional chemical and a
few electrical synapses are present here.
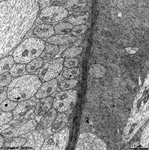
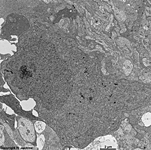
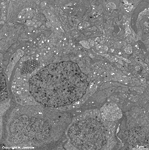
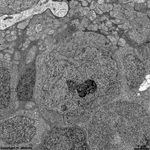
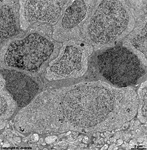
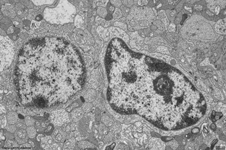
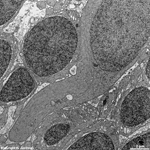
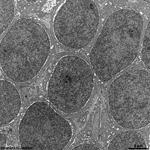
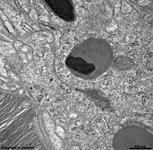
5. inner nuclear layer
= Stratum nucleare internum (--> images)
with perikarya of A. bipolar cells (rod- and cone bipolar
cells = second neurons of the visual pathway which can be further
callsified in many fuctionally different types), B. some amacrine
cells, which are located at the border to 4, C. horizontal
cells, which are also less frequent and located at the border to 6.
Some of the horizontal cells show very large aggregated
macrotubules in their cytoplasm. D.
some intermingeled nuclei of radial fibre cells,
i.e. Müller's glial cells.
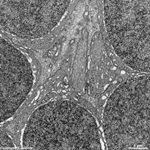
6. outer
plexiform layer = Stratum plexiforme externum (-->
images)
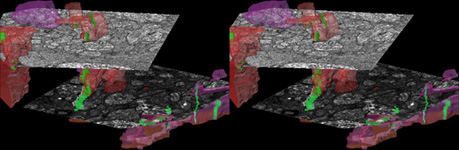
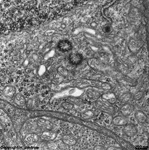
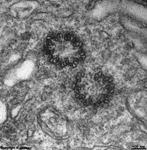
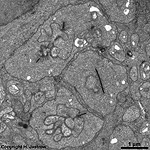
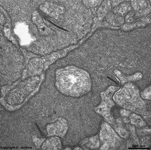
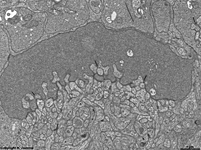
Processes of horizontal and bipolar cells are invaginated into the terminals
of the photoreceptor cells (rods and cones) that show special electron-dense
cell organelles, the synaptic ribbons, close to
their presynaptic membranes in this area.
The resulting ribbon synapses
serve for ultrafast (tonical) signal transduction to the dendrites
of the second neurons of the
visual pathway (rod- or cone bipolar cells). Two bizarrely formed
horizontal cell processes with terminal swellings are present in one invagination
of rod terminals that often is subdivided in two endings. Whereas these
horizontal cell terminals are located laterally, 1 - 3 thin bipolar cell
processes comprise the centre of a ribbon synapse. In contrast to that
cone terminals always show 25 up to over 50 invaginations with usually
two lateral horizontal cell processes around 1 - 2 short bipolar cell dendrites.
Apart from the majority of ribbon
synapses, conventional chemical synapses
are present outside the invaginations. Electrical synapses (gap
junctions) are rare in this layer.
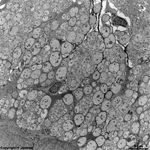
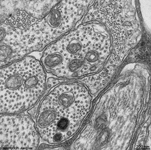
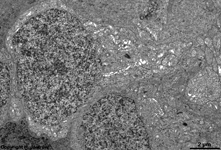
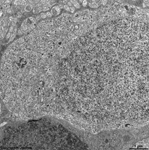
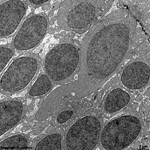
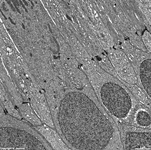
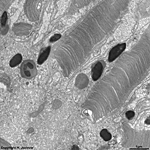
7. outer nuclear layer
=
Stratum
nucleare externum (-->
images) with
the nuclei of the photoreceptor cells
(rods and cones = first neurons of the visual pathway)
8. outer limiting layer
= Stratum limitans externum (--> images)
area with special belt desmosomes (Zonulae
adhaerentes) located between the receptor cells and the very narrow
terminals of Müller's glial cells
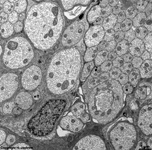
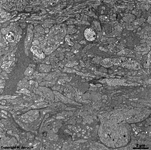
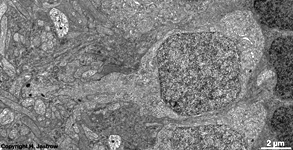
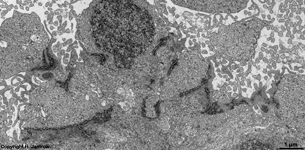
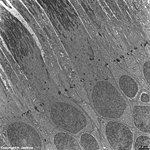
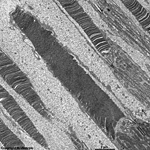
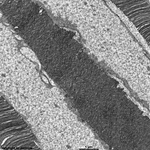
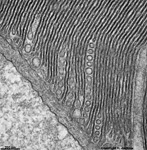
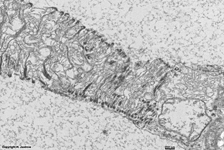
9. layer of inner and
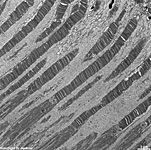
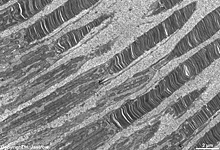
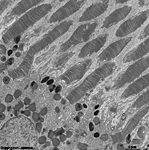
outer segments of rods and cones = Stratum segmentorum externorum
et internorum (-->
images) upper part:
inner-
and lower part: outer segments of rods and cones.
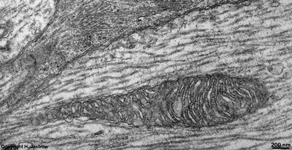
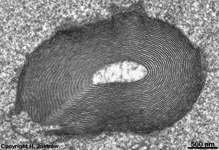
The Ellipsoid is the part of the inner segment of a photoreceptor
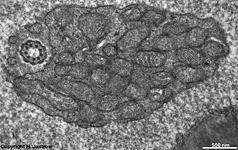
that is closer to the outer segment. It is very rich in mitochondria,
shows some root fibres, wave-like
bundles of intermediate filaments and microtubules.
The ellipsoid continues into the Myoid, the lower part of an inner
segment which is rich in Golgi-apparatuses
and RER but hardly shows any mitochondria.
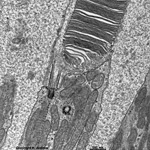
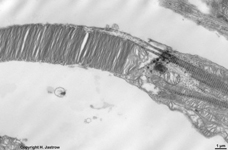
The inner and outer segments are surrounded by a liquor filled space
into which long, thin processes of Müller's glial cells
reach from outside whereas from inside other long, thin processes of pigment
epithelial
cells
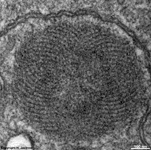
protrude. The outer and inner segments are connected to each other only
via a narrow cytoplasmatic bridge containing
a cilium with 9x2 + 0 microtubules.
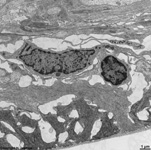
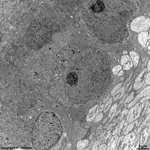
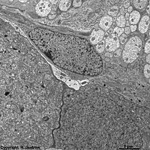
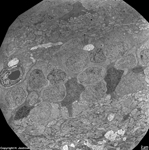
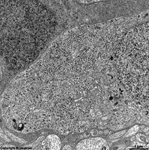
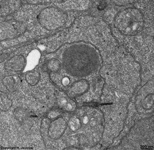
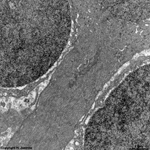
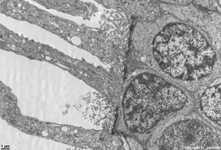
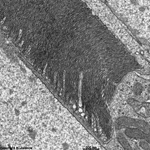
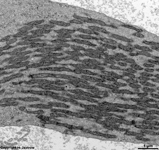
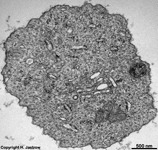
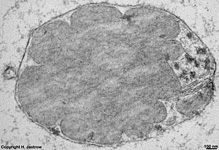
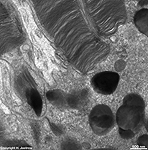
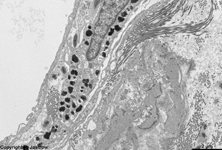
10. pigment epithelium
(Stratum pigmenti = Pars pigmentosa; --> images)
with pigment epithelial cells which phagocyte the tips of the rod
or cone outer segments. The incorporated parts of the outer segments condense
further and finally may no longer be distinguished from nearby pigment
vesicles which prevent reflection of photons from incomeing light.
Vast amounts of smooth endoplasmic reticulum
are characteristic for the cuboid pigment epithelial cells. The junctional
complexes between these cells are rich in tight
junctions and the morphological base for the blood-retina barrier.
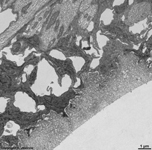
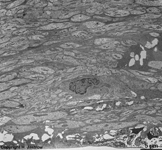
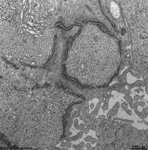
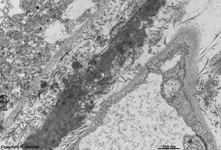
Underlying Bruch's membrane,
a rather thick basement membrane with
lots of elastic and collagen
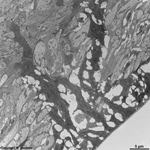
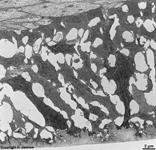
fibres comprises the border to the Lamina choroidocapillaris
(-->
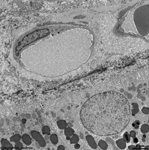
images) which has lots of blood vessels.
The subsequent choroidea shows pigment
epithelial cells scattered in loose connective tissue with an abundance
of smaller blood vessels (especially fenestrated
capillaries
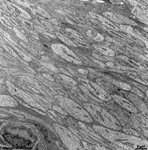
and venoles). The outermost layer of the ocular
bulb is the strong sclera which consists of thousands of very tight
parallel ordered collagen fibre bundles. |