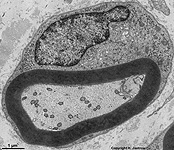
Gliocytus
|
Gliazelle; Hüll- und Stützgewebe des Nervensystems, die der
Isolation und Ernährung von Nervenzellen dienen. Arten von Gliazellen:
PNS: Schwannsche Zellen, ZNS: Astrocyten,
Oligodendrocyten, Ependymzellen
und Mikrogliazellen (Hortega-Zellen). |
Neuroglia cell; a non-nerval cell forming interstitial or supporting
elements of the nervous system. Serves for isolation and nutrition of nerve
cells. Classes of glial cells: PNS: Schwann's
cells; CNS: astrocytes, oligodendrocytes,
ependymal
cells and microglial cells (Hortega). |
Glykokalix

|
Glykokalix; Kohlenhydratbaum an
der Außenfläche der Zellmembran,
sie besteht aus Glykoproteinen, Glykolipiden und Glykosaminoglykanen. Ist
besonders stark an den Mikrovilli des Dünndarms
ausgeprägt. Besteht meist aus zellmembrannaher Isomaltase und darüber
liegender Sucrase an die oben funktionelle Proteine gekoppelt sind. Dort
finden sich spezifische Haftstellen für Antikörper und Hormone
sowie Carboxypeptidase A und B.
--> weitere Abbildungen und Informationen |
Glycocalyx; a thin layer of glycoprotein
and oligosaccharides on the outer surface of cell
membranes that contributes to cell adhesion and forms antigens involved
in the recognition of self. Best formed on microvilli
of the small intestine. Consists of a basal isomaltase, followed by a sucrase
and a superficial functional protein. Possesses binding sites for antibodies
and hormones and has carboxypeptidases A and B.
--> further images and information |
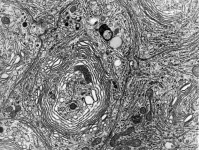
Complexus golgiensis
|
Golgi-Apparat; Zellkernnahe
Zellorganelle aus mehreren hintereinander gelagerten konvex, konkav zusammengefalteten
Doppelmembransäckchen, er kondensiert und verpackt Sekrete, die als
Golgi-Vesikel abgegeben werden. Zudem regeneriert er die Zellmembran.
Ort der Proteinmodifikation (z.B. Kopplung von Proteinen mit Glukoronsäuren).
Empfängt Vesikel aus dem RER an seiner
cis-Seite und gibt an seiner dem RER abgewandten trans-Seite Sekretvesikel
ab. Enthalten diese Sekretvesikel viele Enzyme, werden sie als primäre
Lysosomen bezeichnet, enthalten die Vesikel in sich weitere Bläschen
so heissen diese multivesikuläre Körperchen.
--> weitere Abbildungen und Informationen |
Golgi apparatus; a lamellar membranous
structure near the nucleus of almost all
cells. It consists of curved parallel series of flattened saccules that
are often expanded at their ends. In secretory cells, the Golgi apparatus
concentrates and packs secretory products. The GA serves for regeneration
of the cell membrane; modification
of proteins (e.g. joining of proteins and glucoronic acids). Vesicles of
the RER fuse on the cis-part of the GA. On
its trans-part so called Golgi vesicles are released. If these vesicles
contain enzymes in high concentration they are called primary
lysosomes. If they contain further smaller vesicles, they are called
multivesicular
bodies.
--> further images and information |
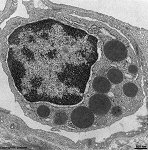
Granulocytus basophilicus
|
basophiler Granulozyt; seltenes weißes
Blutkörperchen
(1-50/µl; 0-1 % der Zellen im Differentialblutbild), beteiligt an
IgE vermittelten Überempfindlichkeitsreaktionen, besitzt im Zytoplasma
dichte basophile
Vesikel, die oft den gelappten
Zellkern
verdecken. Die Vesikel enthalten Histamin, Heparin, Peroxidase und Serotonin.
Obwohl sie den Mastzellen ähnliche
Vesikel
enthalten, ist es nicht nachgewiesen, daß sie sich beim Austritt
ins Gewebe zu solchen umwandeln.
--> weitere Abbildungen und Informationen |
basophilic granulocyte; they are few
of these white blood cells (1-50/µl;
0-1% of cells in WBC).Their nucleus is generally
bilobed, but often obscured by the dark basophilic vesicles
in the cytoplasm. Cells are involved
in IgE mediated allergic reactions. The vesicles contain Histamin, Heparin,
Peroxidase and Serotonin. Though rather similar to mast
cells the latter have not been shown to be the tissue equivalent of
basophilic granulocytes.
--> further images and information |
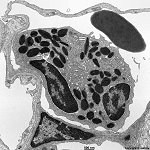
Granulocytus eosinophilicus
|
eosinophiler Granulocyt; relativ seltenes
weißes Blutkörperchen (50-400/µl;
2-4 %) charakteristisch sind die primären
Lysosomen äquivalenten Vesikel mit kristalloiden Strukturen, die
sich mit dem sauren Farbstoff Eosin anfärben lassen. In den Vesikeln
sind im helleren äußeren Bereich lysosomale Enzyme und Peroxidase
und in der kristalloiden Innenstruktur ein cytotoxisch wirkendes „major
basic protein“ enthalten. Sie sind u.a. beteiligt an der Abwehr von Parasiten
und Würmern. Tageszeitabhängige Konzentraton im Blut,
werden chemotaktisch von basophilen Granulocyten
und Mastzellen angelockt und dämpfen
die Histaminwirkung.
--> weitere Abbildungen und Informationen |
Eosinophilic granulocyte; rather rare white
blood
cells (50-400/µl; 2-4% in WBC). They posses specific vesicles
that functionally are primary lysosomes
with crystalloid cores, that can be stained intensely with eosin. The vesicles
contain lysosomal enzymes and peroxidases in the less electron-dense outer
region and cytotoxic major basic protein in the inner cristalloid. Cells
are involved in the destruction of parasites and show diurnal variation
in number. They are chemically attracted by basophilic
granulocytes and mast cells and reduce
histamin effects.
--> further images and information |
Granulocytus neutrophilicus
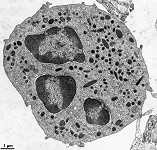
|
Neutrophiler Granulocyt; häufigster
Typ der weißen Blutkörperchen =
Leukozyten (3000-7000/µl; 53-75%), Phagozytose
und oxidative Metabolisierung von Fremdkörpern, zentrale Stellung
bei der Abwehr von Mikroorganismen; kommen als jüngere, stabkernige
(3-5%) und ältere, segmentkernige Zellen (50-70%) vor. Die Zellen
besitzen 2 Typen von Vesikeln, die funktionell primäre
Lysosomen sind: azurophile (lysosomale Enzyme, Peroxidasen) und spezifische
Vesikel (Lysozym, Lactoferrin).
--> weitere Abbildungen und Informationen |
Neutrophilic granulocyte; they are
the most common type of white blood cells
(3000-7000/µl; 43-75%), they contain substances that destroy bacteria
and have a key role in the acute inflammatory reaction, their nucleus
is either bilobed (3-5%) or segmented (50-70%). Cells contain 2 types of
vesicles that functionally are primary lysosomes:
azurophilic (lysosomal enzymes, peroxidases) and specific vesicles (Lysozym,
Lactoferrin).
--> further images and information |
| Granulum |
Körnchen; kleines Körnchen innerhalb einer Zelle, dessen
Umriß klar abgrenzbar, dessen Inhalt jedoch unstrukturiert ist. |
Granule; a small grainlike body, a minute mass in a cell that has an
outline but no apparent structure |
| Granulum chromatini |
Chromatingranulum, eine besonders große und dichte Verklumpung
des Heterochromatins. Chromatingranula
legen sich oft an die innere Kernmembran an. |
Chromatin granule, a larger and dense lump of heterochromatin,
often adjacent to the inner nuclear membrane. |
Granulum glycogeni
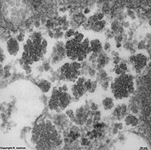
|
Glykogenkörnchen; elektronendichtes
Körnchen das eine Speicherform der Glukose (Gykogen) enthält
und besonders in Leberzellen vorkommt.
--> weitere Abbildungen und Informationen |
Glycogen granule; electron dense
granule containing a storage form of glucose (glycogen); one of the minute
particles of glycogen frequently seen in liver
cells.
--> further images and information |
"Granulum" pigmenti
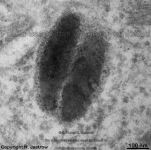
|
die Bezeichnung Pigmentkörnchen ist falsch wird aber immer noch
verwendet, denn tatsächlich handelt es sich wegen der umgebenden Membran
eindeutig um Vesikel. Die Vesikel enthalten meist die Farbstoffe Lipofuszin
oder Melanin. Sie kommen insbesondere in Pigementepithelzellen der Netzhaut
(Retina) oder der Haut, die Melanozyten genannt
werden, vor.
--> weitere Abbildungen |
the term pigment granule is not correct but still in use. Since there
is a membrane around the electron-dense content, the correct term has to
be pigment vesicle. Pigment vesicles contain mostly lipofuscin or melanin
as coloring matter. Typical cells with pingemt vesicles are senn in the
pigment epithelium of the retina and in
skin
where they are termed melanocytes.
--> further images |
--> 










