Overview cell-to-cell contacts
(Junctiones
intercellulares):
Pages with explanations are linked to the
text below the images if available! (Labelling is in German)
|
|
|
|
|
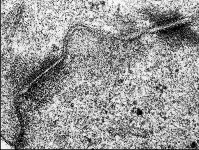
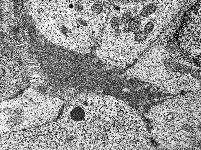
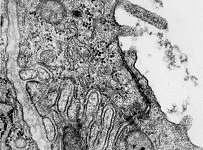
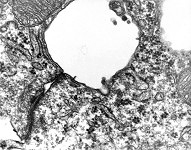
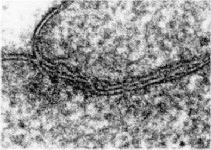
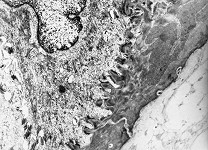
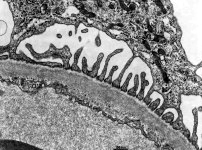
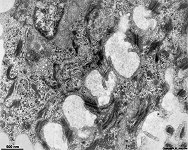
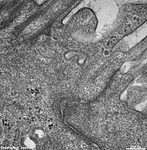
zonula occuldens + adhaerens
human pharyngeal tonsil 1 |
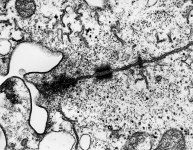
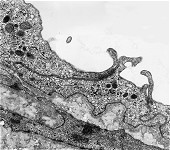
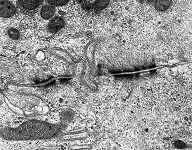
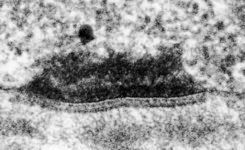
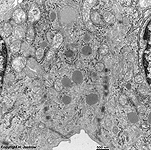
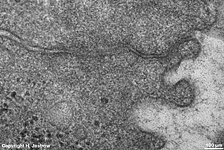
idem + terminal web
human pharyngeal tonsil 2 |
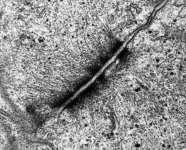
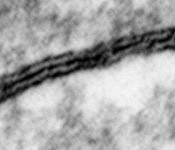
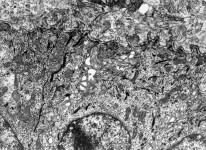
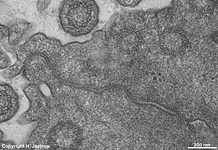
idem human
pharyngeal tonsil 3 |
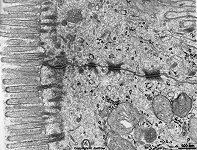
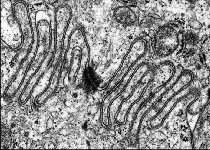
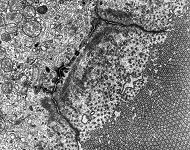
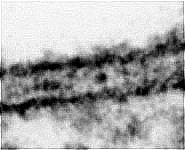
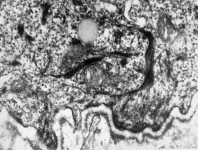
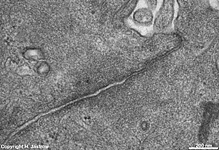
Zonula occuldens et adhaerens
human pharyngeal tonsil 4 |
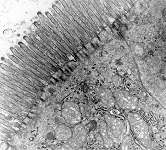
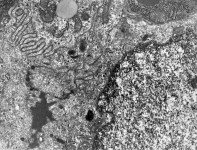
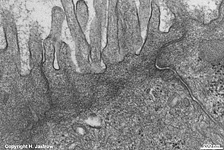
Zonula occuldens et adhaerens
human pharyngeal tonsil 5 |
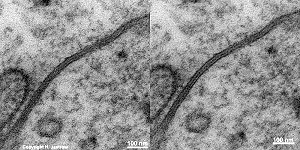
A
A junctional
complex or adhering junction (Terminologia
histologica:
Junctio adhaesionis), which manifests
stable a connection between epithelial cells
consists of (reagrded from the lumen): a tight-junction
(Terminologia histologica: Zonula occludens)
followed in short distance by an adhesive
belt (Terminologia histologia:
Zonula
adhaerens) and one or more spot desmosomes
(Terminologia histologia: Maculae adhaerentes).
All substances that want to pass from the lumen above the epithelium
to the connective tissue and its vessels
below either have to be transported through the cell or much easier
have to bypass them using the very small pores between the
protein-protein connections of the tight-junctions.
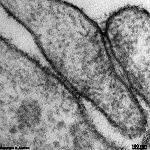
Besides the structures of the junctional complex
there are further cell-to-cell contacts. Information about them can be
retrieved from the pages inked to their names: gap-junction
= nexus; fascia adhaerens, interdigitations,
hemidesmosomes
(anchor to underlaying basement membrane
and connective tissue) and cell contacts that
serve for chemical signal transduction, i.e. synapses
as well as neuromuscular junctions.
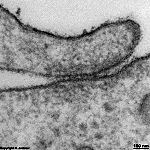
There are simple
intercellular junctions (Terminologia histologica:
Junctiones
intercellulares simplices) where cells just lie side by side and denticulate
intercellular junctions (Terminologia histologica:
Junctiones
intercellulares denticulatae) further those with deeper invaginations i.e.,
digitiform intercellular junctions also called interdigitations(Terminologia
histologica:
Junctiones intercellulares digitiformes). The complex
intercellular junctions (Terminologia histologica:
Junctiones
intercellulares speciales) are even more complicated and present in the
intercalated
disks connecting heart muscle cells. They
consist of interdigitations plus adhesive
strips (Fasciae adhaerentes),
spot desmosomes (Terminologia
histologica: Maculae adhaerentes) and gap-junctions
(Terminologia histologica: Maculae communicantes,
Nexus).
--> interdigitations, gap
junctions, belt desmosome,
tight
junctions, spot desmosomes, fascia
adhaerens, epithelium
--> Electron microscopic atlas Overview
--> Homepage of the workshop
Some images were kindly provided by Prof. H. Wartenberg;
other images, page & copyright H. Jastrow.